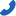
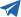
As cooling fan technology continues to evolve, the performance of these fans has become highly sophisticated. With the introduction of new technologies, the applications for cooling fans have also expanded. The market offers fans ranging in size from 8mm to 280mm, with voltage options such as 5V, 12V, 24V, 48V, 110V, 220V, and 380V. Fan designs include square, round, and oval shapes. Based on airflow direction, cooling fans can be classified into four main types: axial fans, mixed flow fans, centrifugal fans, and cross flow fans. Each type has unique designs and applications. Below, we will explore the characteristics and uses of these four types of fans.
1. Axial Fans
Working Principle:
Axial fans move air parallel to the fan's axis, similar to the action of a propeller. When operating, most of the airflow moves in a direction parallel to the fan’s axis, making them ideal for applications requiring high airflow.
Characteristics and Advantages:
- Efficient Cooling: Axial fans provide high airflow at low pressure, ideal for applications that demand efficient cooling.
- Compact Design: Their compact structure makes them suitable for use in electronic devices and industrial enclosures where space is limited.
- Power Consumption Varies with Back Pressure: The power consumption of axial fans increases as the airflow’s back pressure rises, so it’s crucial to select the right fan size and performance for specific applications.
Applications:
Axial fans are commonly used in cabinets, servers, and communication equipment where high airflow is required, such as in electronics cooling, data centers, and industrial equipment.
2. Mixed Flow Fans
Working Principle:
Also known as diagonal flow fans, mixed flow fans combine the design concepts of axial and centrifugal fans. Air enters along the axis of the fan and exits at an angle between the axial and perpendicular directions. These fans typically have a conical blade and housing design, allowing them to deliver high airflow and moderate pressure.
Characteristics and Advantages:
- High Pressure, Low Noise: Mixed flow fans are quieter than axial fans of the same size and provide better airflow under higher pressure conditions.
- Excellent Cooling Performance: Their design allows them to maintain high airflow even under high-pressure conditions, making them ideal for compact devices needing strong cooling.
Applications:
Mixed flow fans are widely used in industrial cooling systems, HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) systems, and other environments requiring high pressure and low noise.
3. Centrifugal Fans
Working Principle:
Centrifugal fans direct air perpendicular to the fan’s axis. While air is drawn in along the axis, it is expelled at a 90-degree angle. This airflow rotation allows centrifugal fans to provide high pressure, making them suitable for applications requiring strong airflow control.
Characteristics and Advantages:
- High Pressure Output: Centrifugal fans offer steady airflow in high-pressure environments, perfect for scenarios requiring high pressure.
- Altered Airflow Direction: Unlike axial fans, centrifugal fans can change the direction of the airflow, making them ideal for applications requiring precise airflow control.
Applications:
Centrifugal fans are used in air conditioning systems, factory ventilation, and boiler ventilation systems that require high pressure and strong airflow, as well as in applications where airflow direction must be controlled.
4. Cross Flow Fans
Working Principle:
Also called tangential fans, cross flow fans move air perpendicular to both the intake and exhaust. They feature long cylindrical blades that provide broad airflow coverage at low rotational speeds, significantly reducing noise.
Characteristics and Advantages:
- Large Cooling Area: The design of cross flow fans enables them to cover a wide cooling area, making them ideal for applications requiring broad surface cooling.
- Low Noise: With their large blades and low rotational speed, cross flow fans operate quietly, making them suitable for noise-sensitive environments.
Applications:
Cross flow fans are commonly used in elevators, air conditioners, and household appliances with wide cooling needs. They are also widely applied in automotive cooling systems.
Conclusion
Choosing the right type of fan depends on the specific requirements and environment of the equipment. Axial fans are ideal for high-efficiency cooling and compact designs; mixed flow fans work well in high-pressure environments; centrifugal fans are suitable for applications needing airflow direction control and high pressure; while cross flow fans are best for cooling wide surfaces. Understanding the characteristics of each fan type can help select the right cooling solution, improving the efficiency and lifespan of the equipment.
If you would like to learn more about cooling fan selection and applications, please contact us. Ruiapple Electric, with 24 years of industry experience, is dedicated to providing high-quality cooling fan products.