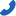
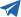
In industrial equipment, electronic cooling, and various other fields, DC fans are essential cooling devices. Whether for efficient heat dissipation or reducing energy consumption while enhancing performance, DC fans play a critical role. When discussing DC fans, two primary types often arise—brushed DC fans and brushless DC fans. These two designs differ in operating principles, performance, and lifespan, each with distinct advantages. Choosing the right fan type is crucial for long-term system stability and efficient operation.
So, what exactly distinguishes brushed from brushless DC fans? What are their respective benefits? This article will explore the key differences between these two types, focusing on their operating principles, performance, lifespan, and suitable application scenarios to help you make an informed decision when selecting a fan.
1. Different Operating Principles: Mechanical vs. Electronic Commutation
The core difference between brushed and brushless DC fans lies in how they operate. Brushed DC fans use mechanical commutators and carbon brushes to switch electrical current. This involves the current passing through carbon brushes to the motor's rotor, driving its rotation. However, the friction between the brushes and commutator leads to wear over time, increasing the likelihood of fan failure. As a result, brushed fans require more frequent maintenance, including periodic brush replacements.
In contrast, brushless DC fans rely on electronic circuits to handle commutation, eliminating the need for carbon brushes. This design avoids mechanical wear, making brushless fans more reliable and less prone to breakdowns caused by component degradation. The electronic commutation not only improves reliability but also allows brushless fans to perform better under high loads and extended operation.
2. Structural and Performance Differences: Universal Motor vs. Squirrel Cage Motor
Brushed DC fans typically use a universal motor, a classic design known for its simplicity and reliability. Due to its straightforward construction, brushed fans are more affordable, making them a popular choice in cost-sensitive applications where low complexity is preferred. They are suitable for environments with lower noise and vibration requirements, and minimal maintenance needs.
Brushless DC fans, on the other hand, usually employ a squirrel cage induction motor, which is more advanced. These motors, controlled electronically, offer precise speed regulation and maintain high efficiency under varying loads. Brushless fans also feature better cooling performance, reduced noise, and lower vibration, making them ideal for applications demanding higher performance and energy efficiency.
3. Lifespan: The Longevity of Brushless Fans
When it comes to lifespan, brushless DC fans clearly outperform their brushed counterparts. Without carbon brushes—components prone to wear—brushless fans can operate for tens of thousands of hours, depending on the type of bearings used. Common bearings include ball bearings and sleeve bearings, with ball bearings offering longer life and more stable performance.
In comparison, brushed fans, while simpler in design, have a shorter lifespan due to brush wear, typically lasting only a few thousand hours. For applications requiring long-term, uninterrupted operation, brushless fans are the better option as they minimize maintenance costs and downtime.
4. Cost and Maintenance: Is the Performance of Brushless Fans Worth the Price?
Although brushless DC fans offer significant advantages in terms of performance and lifespan, their more complex electronic control systems result in higher costs. This can be a concern for projects requiring large quantities of fans, as the upfront investment may be substantial. Additionally, the electronic components in brushless fans can be more susceptible to voltage fluctuations and other external factors, potentially increasing failure risks in extreme conditions. Therefore, it is essential to choose high-quality, rigorously tested brushless fans to ensure stable performance in challenging environments.
5. Application Scenarios: Optimal Uses for Brushed and Brushless Fans
Brushed fans, with their simple structure and lower cost, are often found in applications where performance demands are modest but cost is a priority, such as household appliances and basic ventilation systems. In these cases, short-term cost-effectiveness takes precedence.
Brushless fans, on the other hand, excel in industries where reliability, efficiency, and energy savings are critical. They are commonly used in industrial settings, medical equipment, computers, and data centers. With advancements in brushless technology, these fans are increasingly being applied in cutting-edge fields like electric vehicles, wind power, and smart home systems.
Conclusion
Understanding the key differences between brushed and brushless DC fans can help you make better decisions. Brushed fans are suitable for low-cost, short-term applications with simple maintenance needs. However, for high-performance, energy-efficient, and long-lasting applications, brushless fans are the clear choice, offering superior reliability despite their higher initial investment.
As a leading manufacturer in the cooling fan industry, Ruiapple Electric offers a wide range of both brushed and brushless DC fans. With 24 years of production experience, we are committed to delivering customized, high-performance cooling solutions. If you have any questions or needs regarding DC fans, please contact us, and we will provide expert advice and services.