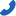
When selecting the right cooling fan, understanding the differences in power types, performance, and application scenarios for AC, DC, and EC fans is essential. Each type offers unique advantages for efficiency, energy use, and noise control. Here’s an in-depth look at the operating principles, benefits, and ideal applications for each fan type, helping you make an informed decision.
AC Fans (Alternating Current Fans)
Advantages:
- Lower Cost: Simple design and manufacturing make AC fans cost-effective for general applications.
- Ease of Maintenance: The straightforward structure allows for low maintenance, ideal for scenarios that don’t require precise speed control.
Disadvantages:
- Fixed Speed: AC fan speed is tied to grid frequency, making adjustment difficult.
- Higher Energy Consumption: Generally, they consume more power than DC fans of comparable performance.
- Higher Noise Levels: Operating at a fixed speed can lead to higher noise, limiting AC fans in noise-sensitive environments.
DC Fans (Direct Current Fans)
Advantages:
- Energy Efficiency: DC fans offer high energy efficiency, ideal for battery-powered devices.
- Low Noise: Silent design and speed control make DC fans quieter than AC fans.
- Precise Speed Control: Adjustable speed is suitable for temperature-sensitive applications like electronics and data centers.
Disadvantages:
- Higher Cost: Manufacturing costs are higher than for AC fans, suited for specialized equipment requiring speed control.
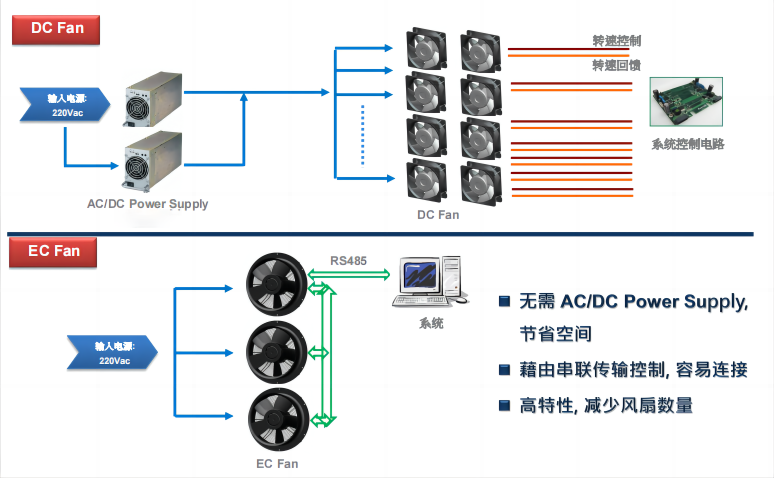
EC Fans (Electronically Commutated Fans)
Advantages:
- Intelligent Control: Capable of real-time monitoring and dynamic adjustments for precise speed control based on environmental needs.
- Energy Efficiency: EC fans achieve superior energy conversion efficiency compared to AC and DC fans under varying loads.
- Low Noise, Long Lifespan: The intelligent control reduces noise and extends fan lifespan, ideal for demanding environments requiring high-efficiency, intelligent cooling.
Disadvantages:
- Higher Price: The complex electronic control system typically results in higher costs.
Selection Recommendations
The right fan depends on your cooling needs. For basic ventilation, AC fans are a cost-effective choice, while DC fans are better for applications requiring noise control and energy efficiency. EC fans are ideal for high-end applications that require intelligent control and precise cooling, such as data centers, medical equipment, and electric vehicle charging stations.
As an experienced cooling fan manufacturer, Ruiapple Electric offers a variety of AC, DC, and EC fans, supporting custom solutions to meet diverse cooling needs. If you’re looking for a high-performance, low-noise, and energy-efficient cooling solution, contact Ruiapple Electric to find the ideal fan for your requirements.