Airflow is a key parameter in assessing the cooling performance of a fan. Accurately calculating airflow when designing or selecting a fan helps ensure that it meets cooling requirements. Below is a detailed explanation of how to calculate airflow, including formulas and relevant applications.

- What is Airflow?Airflow refers to the volume of air the fan moves per unit of time, usually measured in CFM (Cubic Feet per Minute) or CMM (Cubic Meters per Minute). A larger airflow indicates greater air movement capacity, which leads to more efficient heat dissipation.
- Formula for Calculating Cooling AirflowCooling airflow can be derived using the law of energy conservation:
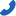
Heat dissipation formula:
Where:
- H = Heat dissipation (in watts)
- C = Specific heat capacity of air (typically 1005 J/(kg·K))
- m = Air mass flow rate (in kg/s)
- Δt = Temperature rise (in Kelvin)
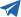
Air mass flow rate formula:
Where:
- ρ = Air density (1.2 kg/m³ at standard conditions)
- Q = Airflow (in CMM)
- t = Time (in seconds)
The airflow formula becomes:
Given:
- H = 100W
- Δt = 10°C
- C = 1005 J/(kg·K)
- ρ = 1.2 kg/m³
Using the formula:
Q = 100 1005 ⋅ 1.2 ⋅ 10 Q ≈ 0.0083 m³/ s ≈ 29.4 C F M
Therefore, to meet the cooling demand, the fan needs to provide at least 29.4 CFM.
- Relationship Between Temperature Difference and AirflowAirflow is inversely proportional to the temperature difference. When the temperature difference is large, the required airflow is smaller. Conversely, a smaller temperature difference requires a higher airflow to dissipate heat. For example, with a temperature difference of 2°C, the required airflow would significantly increase, which is critical in high-heat-density scenarios.
Factors Affecting Airflow Calculation
- Ambient Temperature: Higher ambient temperatures reduce cooling efficiency, requiring a larger airflow to compensate.
- System Impedance: High impedance reduces the effective airflow, so fans with higher static pressure must be selected to overcome resistance.
- Fan Efficiency: Actual airflow is often lower than theoretical values, so fan design and manufacturing precision must be considered.
- How to Choose the Right Cooling Fan
- Match Power and Temperature Difference Requirements: Use the above formulas to calculate the cooling demand and select a fan that meets the required CFM.
- Consider Static Pressure and Noise: Larger airflow often comes with higher noise and static pressure, so balance these factors according to the application.
- Consult Anpu Electric Product Specifications: Anpu Electric offers a wide range of cooling fans with varying airflow capabilities to meet complex application needs.
- Tools and Platforms to Improve EfficiencyRuiapple Electric is dedicated to providing comprehensive fan knowledge and solutions. You can visit our website to access professional calculation tools and explore technical articles to quickly learn how to select and apply cooling fans.
By following the above methods and examples, you can accurately calculate the required airflow for cooling fans and choose the appropriate product to enhance system reliability and cooling efficiency. Anpu Electric helps you achieve superior cooling performance!