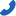
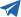
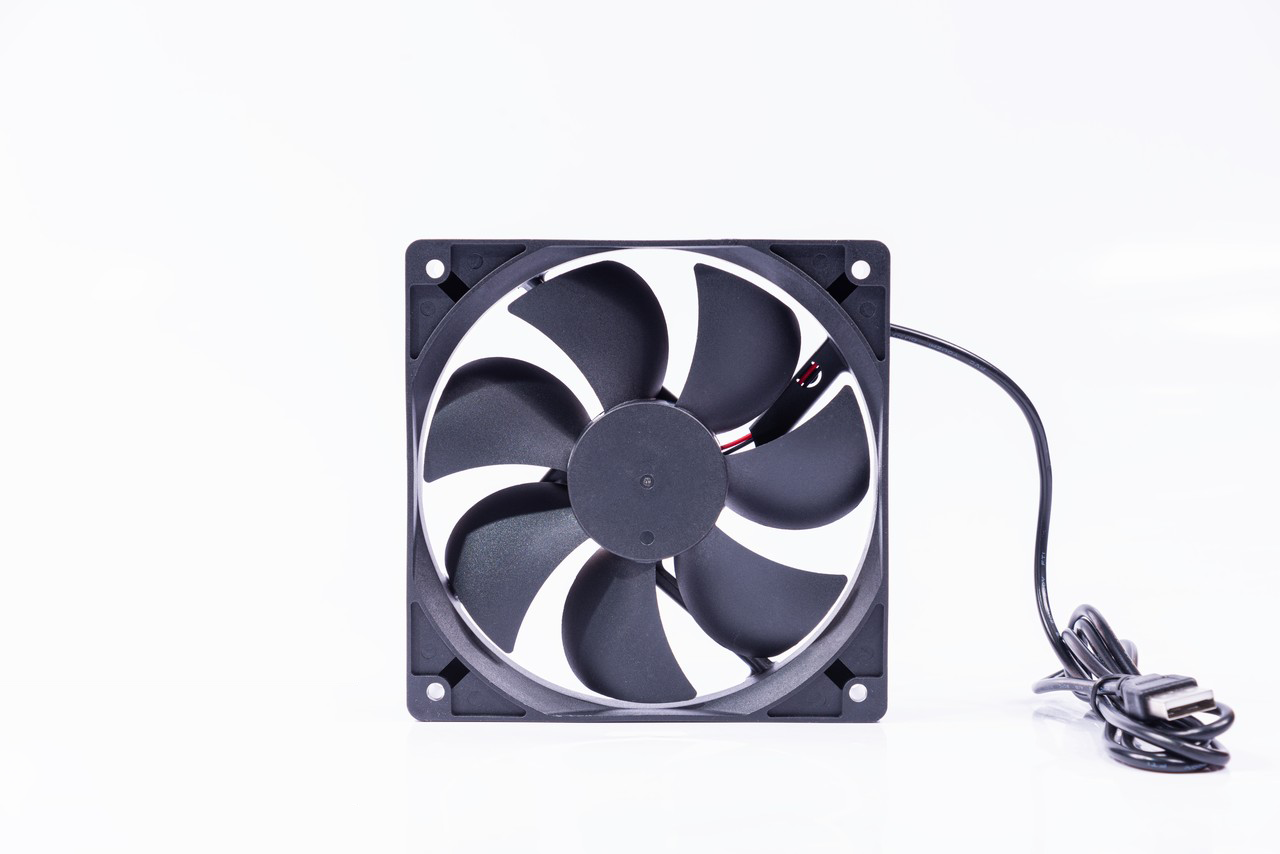
In modern society, cooling fans are essential electronic devices, widely used across various industrial sectors, particularly in the cooling of high-density electronic products and equipment. Whether for computers, communication devices, or new energy vehicles, cooling fans play a crucial role. Below is an overview of the manufacturing process of cooling fans, from material preparation to final product dispatch, with each step carefully controlled to ensure product quality and performance.

1. Material Preparation and Process Planning
Before production begins, it's essential to ensure that all materials are ready and a detailed process flow chart is established. This step forms the foundation of the entire manufacturing process, and all subsequent steps must strictly follow the outlined standards.
2. Winding
Winding is one of the key steps in the manufacturing process of cooling fans. Precision winding machines are used to wind coils evenly, ensuring uniformity and avoiding electrical shorts or performance instability. High-precision winding effectively improves the fan's operational efficiency and lifespan.
3. Stator Impedance Testing
Stator impedance testing is crucial to ensuring motor performance. An impedance tester is used to check the winding for potential electrical faults, ensuring readiness for assembly and performance testing.
4. Wire Separation
After successful stator testing, the wire separation process follows. Wire cutters are used to separate different wires for subsequent welding and assembly.
5. Pin Dip Soldering
In this step, pins are dipped in a soldering furnace to ensure good soldering quality and improve connection reliability. Accurate temperature control is required to prevent overheating or poor soldering.
6. Inserting and Pressing ICs
ICs (Integrated Circuits) are inserted into the circuit board, and a dedicated IC press is used to ensure firm, precise connections between the ICs and the board.
7. Inserting Diodes, Resistors, and Capacitors
Diodes, resistors, and capacitors are individually inserted into the circuit board and properly installed. These components are crucial for the stability and efficiency of the cooling fan, and correct installation is essential.
8. Soldering Components
Once all components are inserted, they are soldered using a soldering furnace to ensure reliable electrical connections. Magnetic boards are often used for alignment to prevent component misplacement.
9. Inserting the Coil into the PCB
The coil is carefully inserted into the PCB (Printed Circuit Board), and anti-static rings are used to prevent static damage to the components during handling.
10. Transferring the PCB to the Fixture
The PCB with the inserted coil is transferred to a specialized fixture, where fine-tuning is done with tweezers and clippers to ensure proper alignment for the next welding step.
11. Soldering the Stator
The stator is soldered using a soldering iron, a stator fixture, and anti-static rings. As a key component of the motor, the quality of the stator soldering directly affects the fan's efficiency and stability.
12. Visual Inspection
After all soldering steps are completed, a visual inspection is performed. Anti-static rings and other tools are used to ensure the fan is free from defects, and all components are properly soldered.
13. Stator Performance Testing
The stator is tested for electrical performance using an oscilloscope, power supply, and testing fixture, ensuring it meets design standards and validating the fan's proper functioning.
14. Soldering Wires
Wires are soldered using a temperature-controlled soldering iron and anti-static rings to ensure stable electrical connections and prevent wire contact issues or component damage due to overheating.
15. Applying Structural Adhesive to the Stator
Once the stator is assembled, structural adhesive is applied to secure the middle tube, ensuring the stator and other parts are firmly connected, preventing vibration or friction damage.
16. Wiring the Stator
Using anti-static rings, the stator’s wiring is organized to ensure optimal electrical layout, enhancing the fan’s cooling efficiency and operational stability.
17. Pressing the Stator
A pneumatic press is used to compress the stator, ensuring the components are tightly secured. During this process, pressure must be carefully controlled to avoid component deformation due to excessive force.
18. Pressing the Fan Blades into the Motor Housing
The fan blades are pressed into the motor housing using a pneumatic press, ensuring a tight connection between the rotating components and the motor to enhance operational efficiency.
19. Rust Prevention on the Shaft
Anti-rust oil is applied to the shaft to prevent metal parts from rusting over time. Gloves are worn during this step to avoid direct contact with the oil.
20. Installing Springs and Bearings in the Fan Blades
Springs and bearings are installed in the fan blades using a spring installation machine and bearing assembly fixture. Precision and consistency are crucial to ensure the fan’s balance.
21. Assembling the Fan Blades and Outer Frame
The fan blades are assembled with the outer frame, ensuring precise alignment of all parts and maintaining both the fan’s appearance and functional stability.
22. Installing the Rear Bearings
Rear bearings are installed to ensure smooth fan blade rotation and minimize frictional wear.
23. Installing the Retaining Ring
A retaining ring is installed on the cooling fan’s outer components using a retainer tool, ensuring all parts are securely fixed and preventing loosening during operation.
24. Final Product Testing
The final product undergoes a functional test using a stable power supply and testing board to ensure that all performance parameters meet quality standards and confirm its reliability.
25. Labeling
Labels are applied to the products, indicating model numbers, technical parameters, and production dates. This step is performed with precision to ensure the labels are wrinkle-free.
26. Packaging
The tested and qualified products are packaged securely to ensure safe transport. Packaging materials are eco-friendly and provide sufficient compression resistance.
27. Quality Assurance (QA) Inspection
After the production process is completed, a final QA inspection is conducted using a stable power supply, test board, and computer testing instruments to ensure the fan meets all performance criteria and customer requirements.
28. Storage
Once testing and packaging are finished, the cooling fans are stored on shelves, awaiting dispatch to customers. Inventory is categorized and managed for quick and efficient future shipping.
The production process of cooling fans is both meticulous and complex, covering every stage from raw material procurement to the final product. Each detail is tightly controlled to ensure every fan provides stable, high-performance cooling. Through precise testing and meticulous assembly, Ruiapple Electric’s cooling fans deliver reliable, long-term performance across various applications, offering customers consistent and dependable results.